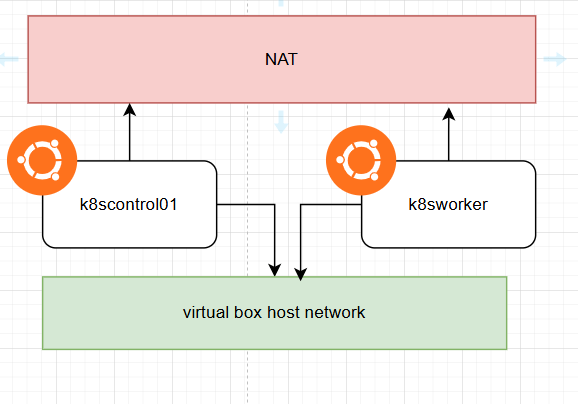
I’m working on containerizing web/was servers to my company’s k8s environment. In order to do that, I have to configure docker files ,make docker images, save them in .tar format, scp-ing to the k8s server and import docker image to containerd. But everytime I find the modification, I need to reconfigure the docker image and follow the stressful process I mentioned.
In order to stop doing that, I decided to configure docker private registry in my envirionment.
docker pull image registry
After the pulling is done, you can check the downloaded image.
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --name dockerregistry registry:latest
After the creation of the container, you can see the running container by using “docker ps” command.
docker image tag omniwebbase:v1.0.0 10.0.7.6:5000/omniwebbase:v1.0.0
you can see the uploaded image with a tag
what I’m trying to do is configuring registry where I can pull images pushed to the registry server seperated from k8s server. In order to do that, I will modify my containerd’s config.toml.
config.toml file is in the /etc/containerd/config.toml path.
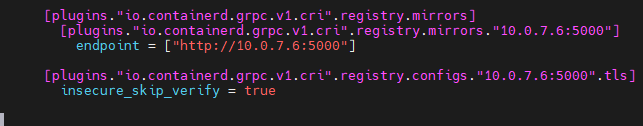
you need to add the address of the registry server, If you use the http access with no tls certificate, you need to add insecure_skip_verify option with a value true.
And also you need to modify docker’s daemon.json file. It’s in /etc/docker/daemon.json directory

It’s for pushing images to registry server. If you don’t configure this option, you will get HTTP response error.
docker image push 10.0.7.6:5000/<image>
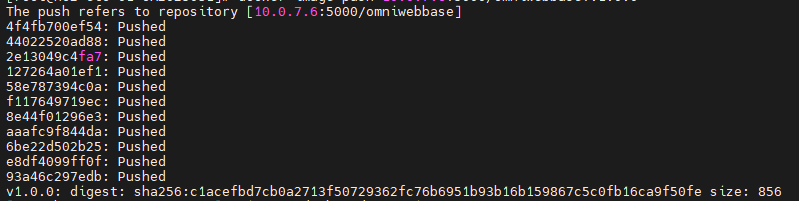
you can see the pushing process is working fine.

you can see if the registry is approachable by usign curl. If it’s working fine, your docker registry is ready to use.